
Saturday August 19th is World Photo Day! Spectroscopy adds a deeper level of understanding and analysis to the science of photography, allowing us to explore and appreciate the world beyond what is visible to the naked eye.
Spectral Imaging
Spectroscopy plays a role in spectral imaging techniques, where cameras capture images at different wavelengths across the electromagnetic spectrum. Instead of traditional RGB (Red, Green, Blue) images, spectral imaging records data at specific wavelengths, allowing scientists and researchers to analyze the spectral characteristics of the light captured by the camera. Check it out!


Astronomy and Astrophotography
Spectroscopy is extensively used in astronomy and astrophotography. Astronomers use spectrographs, specialized instruments, to split light from celestial objects into its constituent colors, creating spectra. These spectra provide valuable information about the composition, temperature, and velocity of stars, galaxies, and other celestial phenomena! Astrophotographers also use spectroscopy to analyze the light emitted by distant objects, aiding in their understanding of the universe.
Color Calibration and Reproduction
Spectroscopy is used in the calibration and reproduction of colors in photography. Color management systems often rely on spectrophotometers to measure and analyze colors accurately. By calibrating cameras, monitors, and printers using spectral data, photographers can ensure that the colors in their images are reproduced faithfully across different devices and printing processes.

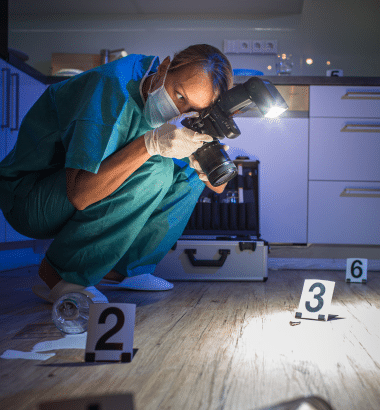
Forensic Photography
Spectroscopic techniques such as infrared, UV-Vis, and Raman help aid in the identification of chemical compositions, especially for substances not visible to the naked eye. Forensic photography captures the physical context and characteristics of evidence, particularly for trace materials like fibers or paint chips. The combination of spectroscopic analysis and photographic documentation enhances investigations with comprehensive insights, strengthening court presentations, and leading to more accurate and effective forensic conclusions.
Art Authentication
In the field of art conservation and authentication, spectroscopy is used to analyze pigments and materials used in paintings or photographs. By studying the spectral characteristics of the artwork, experts can determine its authenticity, age, and even identify potential restoration attempts. Spectroscopy can provide valuable insights into an artwork’s composition, allowing for better preservation and restoration strategies.

The science behind taking photos is a mesmerizing combination of optics, light manipulation, electronics, and digital wizardry. The process of capturing light and transforming it into vivid memories is a fascinating journey that bridges the gap between art and science. Next time you press the shutter button, take a moment to appreciate the intricate science at work, allowing you to preserve the beauty of the world and create lasting memories!📸





