K. Maciejewska & L. Marciniak
Published: 10 January 2023
Abstract
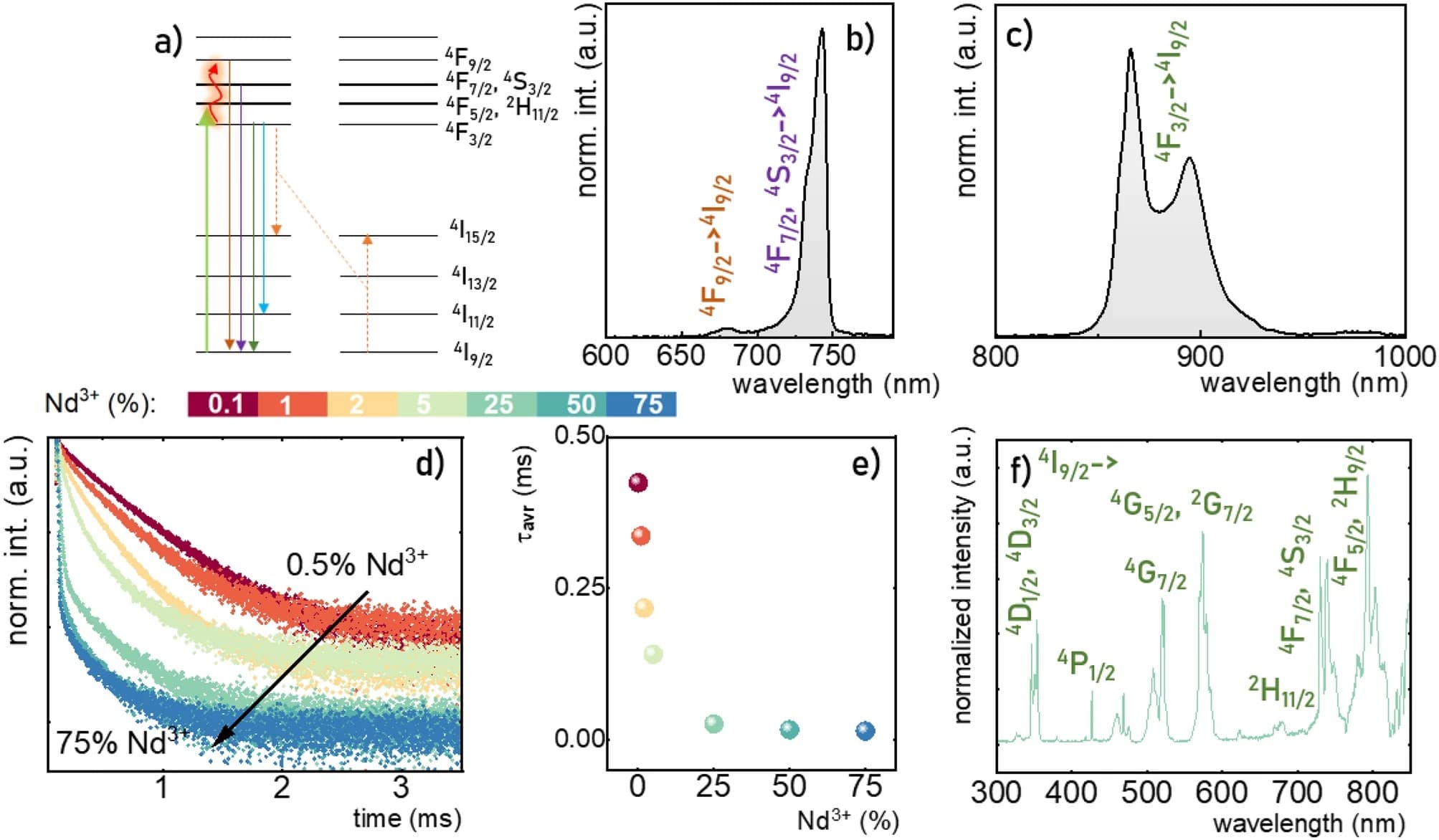
The growing popularity of luminescence thermometry observed in recent years is related to the high application potential of this technique. However, in order to use such materials in a real application, it is necessary to have a thorough understanding of the processes responsible for thermal changes in the shape of the emission spectrum of luminophores. In this work, we explain how the concentration of Nd3+ dopant ions affects the change in the thermometric parameters of a thermometer based on the ratio of Stokes (4F3/2 → 4I9/2) to anti-Stokes (4F7/2,4S3/2 → 4I9/2) emission intensities in NaYF4:Nd3+. It is shown that the spectral broadening of the 4I9/2 → 4F5/2, 2H9/2 absorption band observed for higher dopant ion concentrations enables the modulation of the relative sensitivity, usable temperature range, and uncertainty of temperature determination of such a luminescent thermometer.
The anti-Stokes (a); and Stokes (b) parts of emission of NaYF4:1%Nd3+ nanoparticles upon 808 nm excitation; the impact of the concentration of Nd3+ ions on thermal evolution of normalized integral emission intensities of 4F3/2 → 4I9/2 (c) and 4F7/2,4S3/2 → 4I9/2 (d) emission bands of NaYF4: Nd3+ nanoparticles; the temperature dependent LIR values of NaYF4:Nd3+ nanoparticles (e); the corresponding SR (f).
… The emission spectra were recorded using 808 nm excitation lines from laser diode (LD of 1.1 W/cm2 excitation density) and a Silver-Nova Super Range TEC Spectrometer from Stellarnet (1 nm spectral resolution) as a detector …






